
What are the differences between Rvv sheath wire and THHN wire, as well as the characteristics and advantages
2022-08-11 16:27The difference between RVV sheath wire and THHN wire
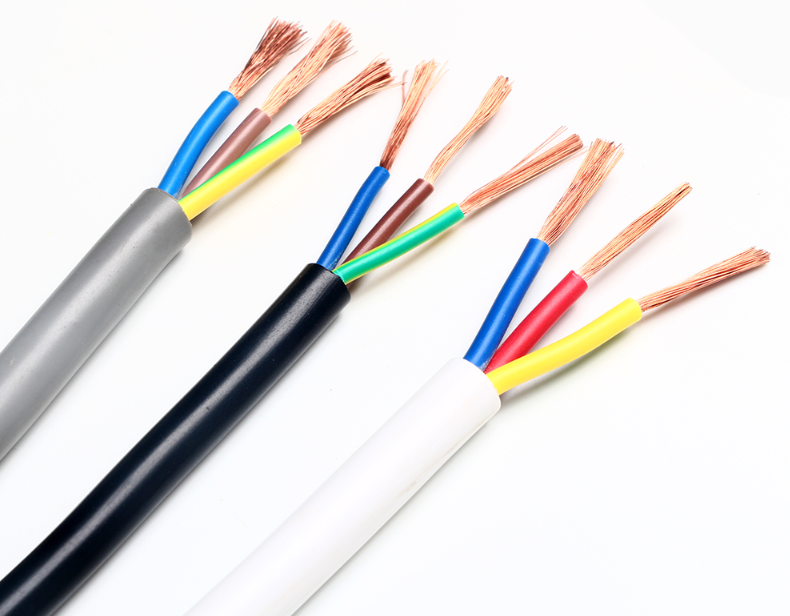
Rvv sheathed wire: Rvv sheathed wire can also be used for general purposes such as wiring circuits, machine tools and appliances, and is an excellent alternative to the traditionally used THHN wire as it is safer and lasts longer. The main purpose of RVV sheath line is to locate buried gas pipelines and various machines and equipment. It can also be used for underground positioning line, positioning line and other environments.
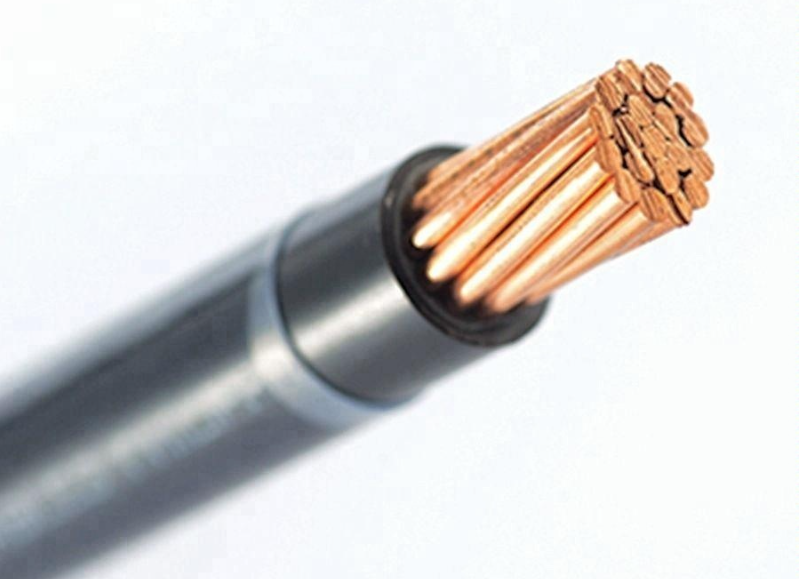
THHN Wire: Thermoplastic high heat resistant nylon (THHN) is a general purpose wire for machine tools and some electrical appliances, but its main use is as construction wire. THHN wires are used to transmit electricity throughout the building. THHN wires are not approved for underground burials.
THHN stands for thermoplastic high heat resistant nylon. The wire itself is either copper or aluminum (both electrical conductors), twisted or solid. THHN wires are then coated with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) followed by nylon sheathing.
RVV sheathed wire is similar to THHN wire, and TH stands for thermoplastic heat resistance. The "W" added to THW indicates that the wire is also waterproof. The tracer is coated with polyethylene to make it waterproof.
The sheath layer of RVV sheath wire is thicker than the nylon sheath layer of THHN wire, lasts longer, and is more resistant to elements. Therefore, the RVV sheath line is the best choice for durability and is likely to withstand the service life of the work it is used for. THHN wires often need to be replaced because they corrode or no longer transmit.
THHN wires are approved to withstand voltages of up to 600 volts to meet most residential and industrial electricity needs. It can reach temperatures of up to 90 degrees Celsius in dry environments. Unless it is THWN rated, THHN wire does not perform well in wet environments. The nylon sheath layer gives the wire flexibility, which is essential for wiring and wiring requirements.
RVV sheathing lines are also approved for use up to 600 volts and perform well at temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius. It has a range of 8-14 AWG.
Due to its polyethylene coating, the RVV sheathed line can withstand temperatures up to 75 degrees Celsius in humid conditions. The outer layer also provides resistance to corrosion, water damage, and exposure to natural gas and oil. That's why it's great for locating gas and water lines.
RVV sheathed wires can withstand higher temperatures in humid conditions, last longer, and are more dangerous than THHN wires.
Rvv sheathed wire with THHN wire cost
THHN wire is cheaper than RVV sheathed wire; This contributed to its popularity as a building wire. In some residential, industrial, or construction scenarios that require a lot of construction wire, THHN wire is a logical choice because of the significant cost savings.
However, problems arise when contractors select THHN for applications that are better suited to RVV sheathing lines. Contractors may see initial cost savings, but ongoing repair, maintenance, and replacement costs quickly turn those immediate savings into large losses in the long run.
Rvv sheathing lines have the potential to be dangerous, and when low-quality lines are not correctly chosen for the job, THHN wires quickly become obsolete, as tracer lines are now a safer and more accessible option for general wiring needs.
